
Edge AI using LLMs
Active ProjectMachine Learning
This project explores the deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) on the NVIDIA Orin Nano Super — a powerful yet compact edge computing platform. The goal is to assess performance, latency, and real-world usability of AI inference workloads in constrained environments. It combines hardware acceleration with software optimization to demonstrate intelligent edge solutions capable of processing natural language locally, without relying on cloud infrastructure. This research provides foundational insight for building secure, low-latency AI systems for robotics, IoT, and offline applications.
11
Total Feedback
Feb 7
Last Updated
Key Features
HardwareAI/MLSoftware
Tech Stack
LLMNVIDIA Jetson Orin NanoONNX Runtime / TensorRTPython+5 more
Image Gallery
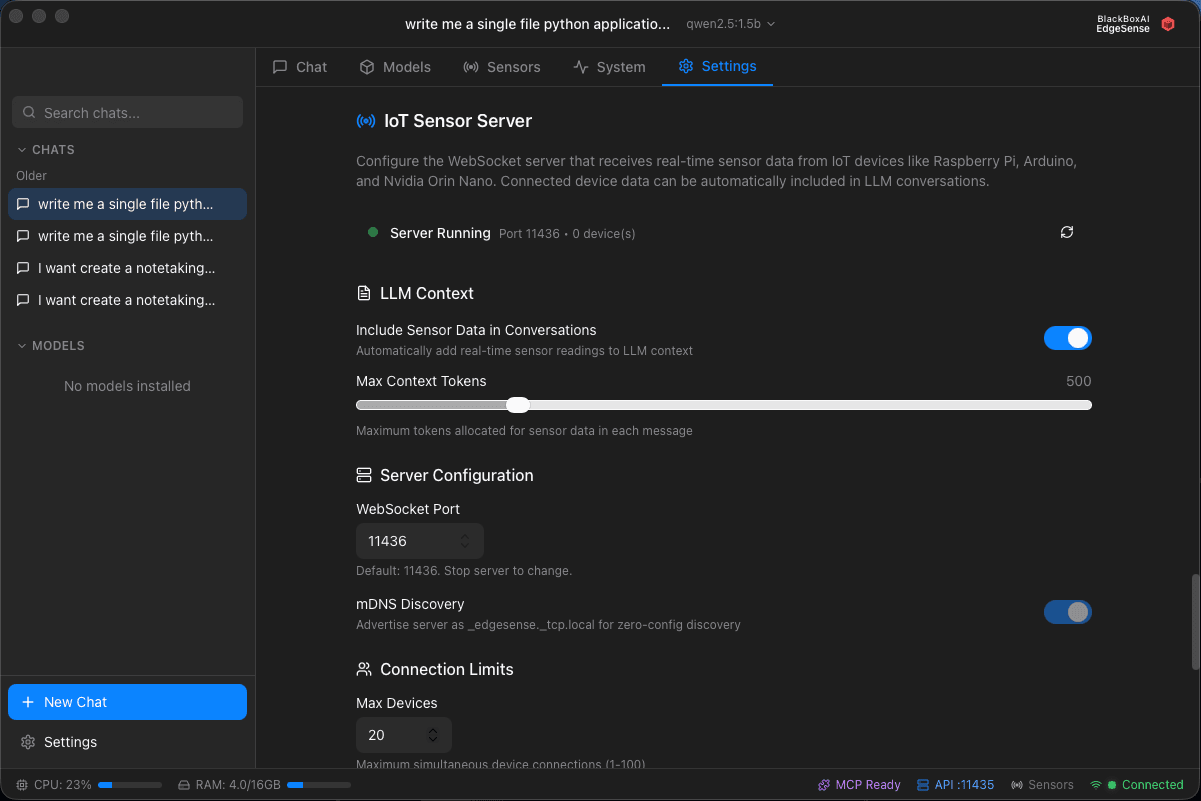
EdgeSense Sensor Data - Settings
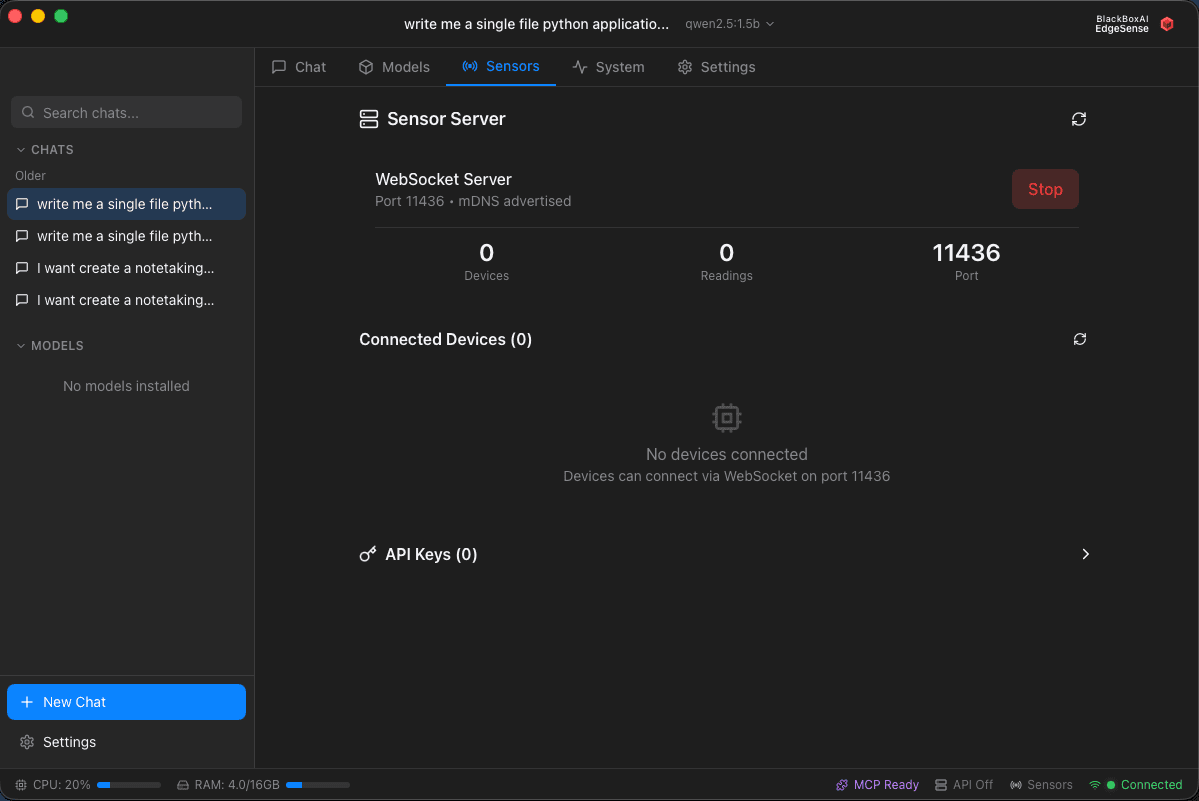
EdgeSense Sensor Data - Discovery

EdgeSense - Chat Window
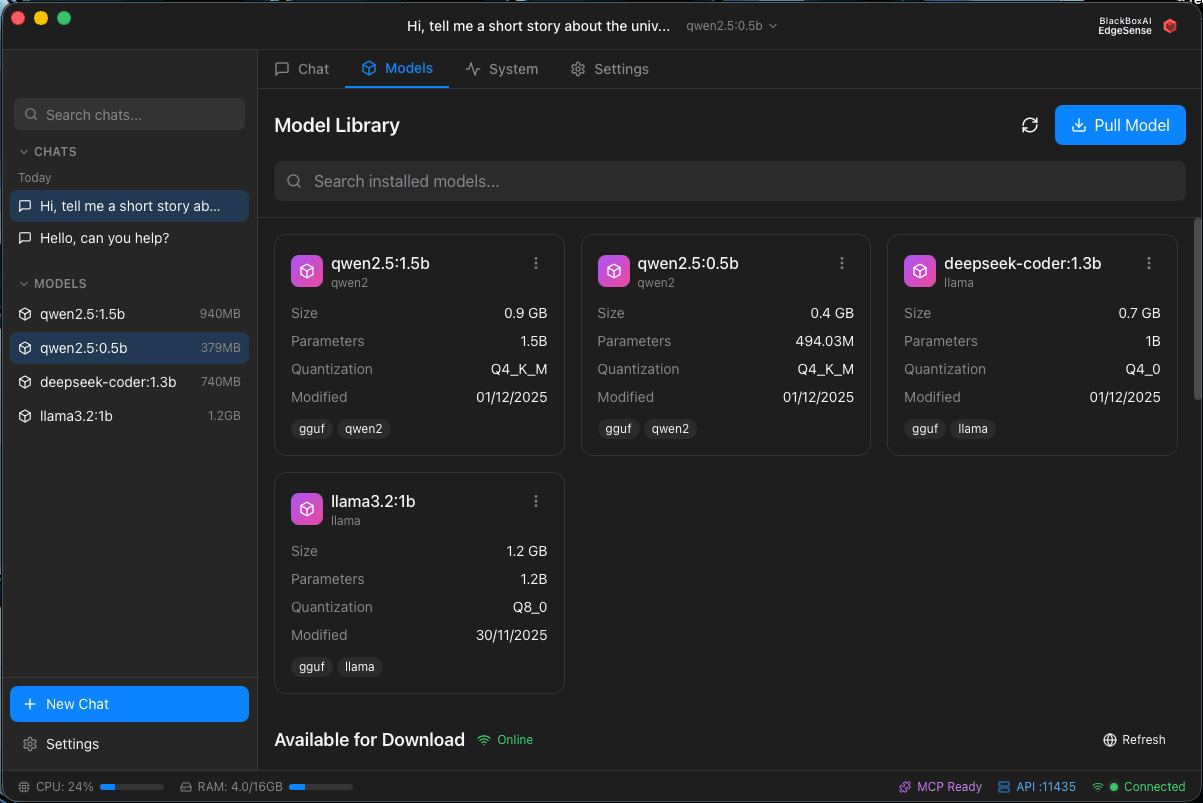
EdgeSense - Available and Download Models
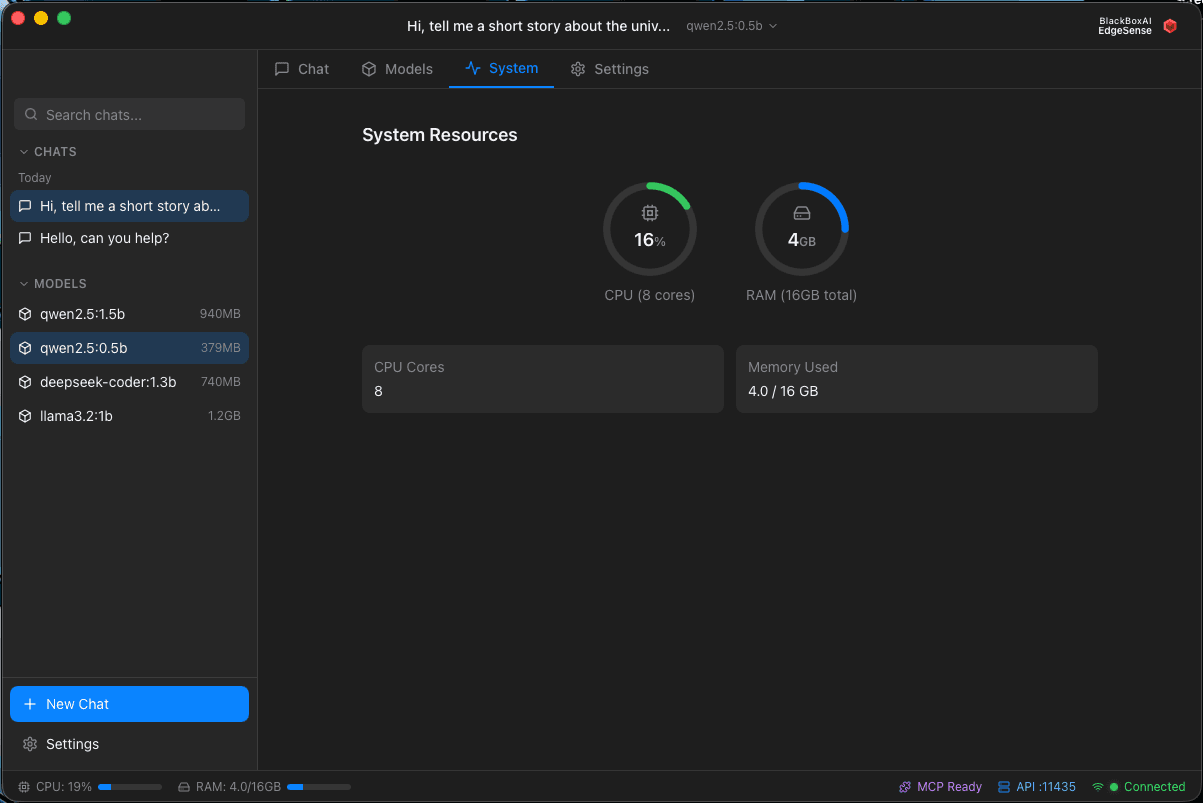
EdgeSense - System Performance
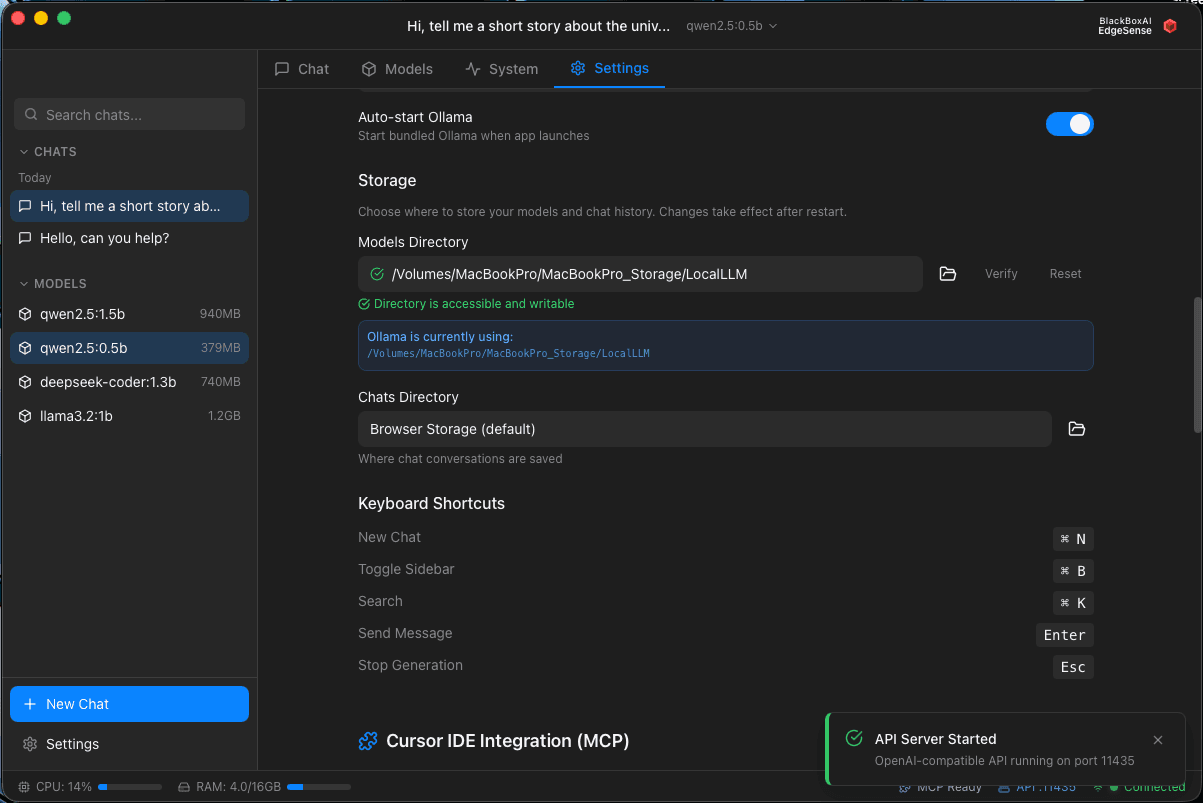
EdgeSense - Setting Page
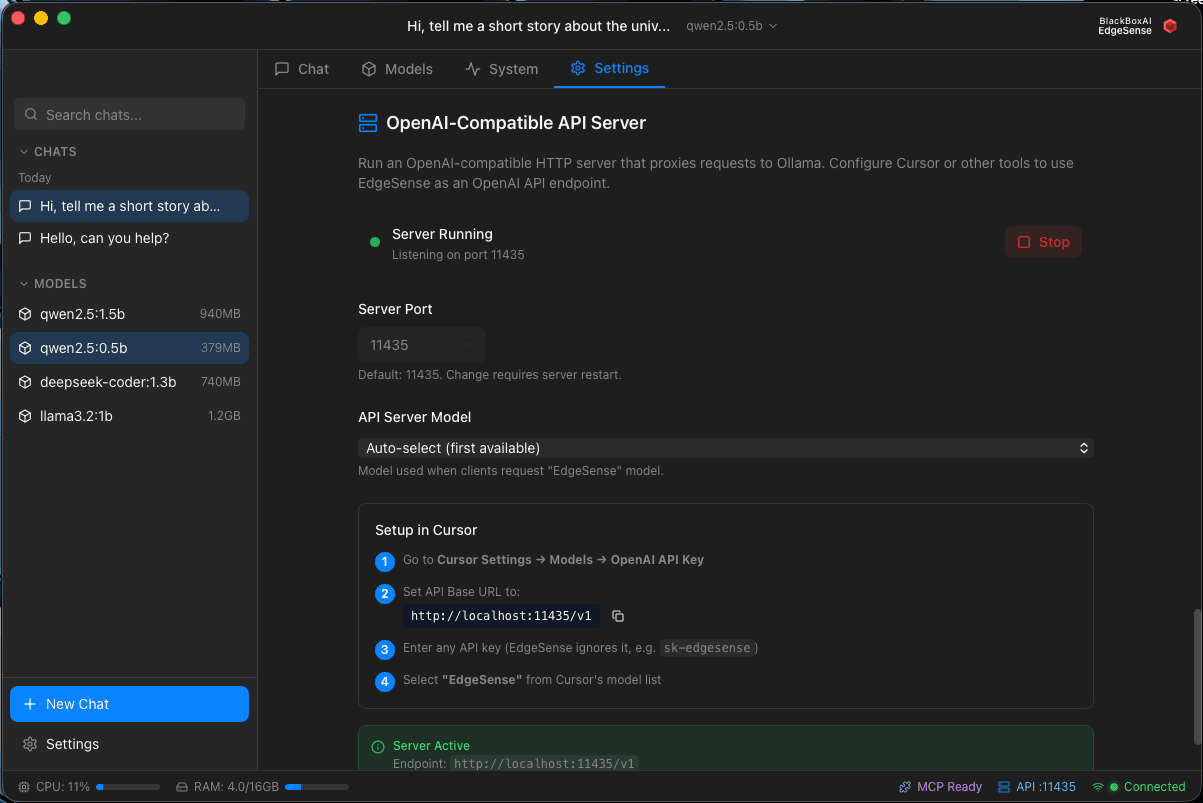
EdgeSense - API Server
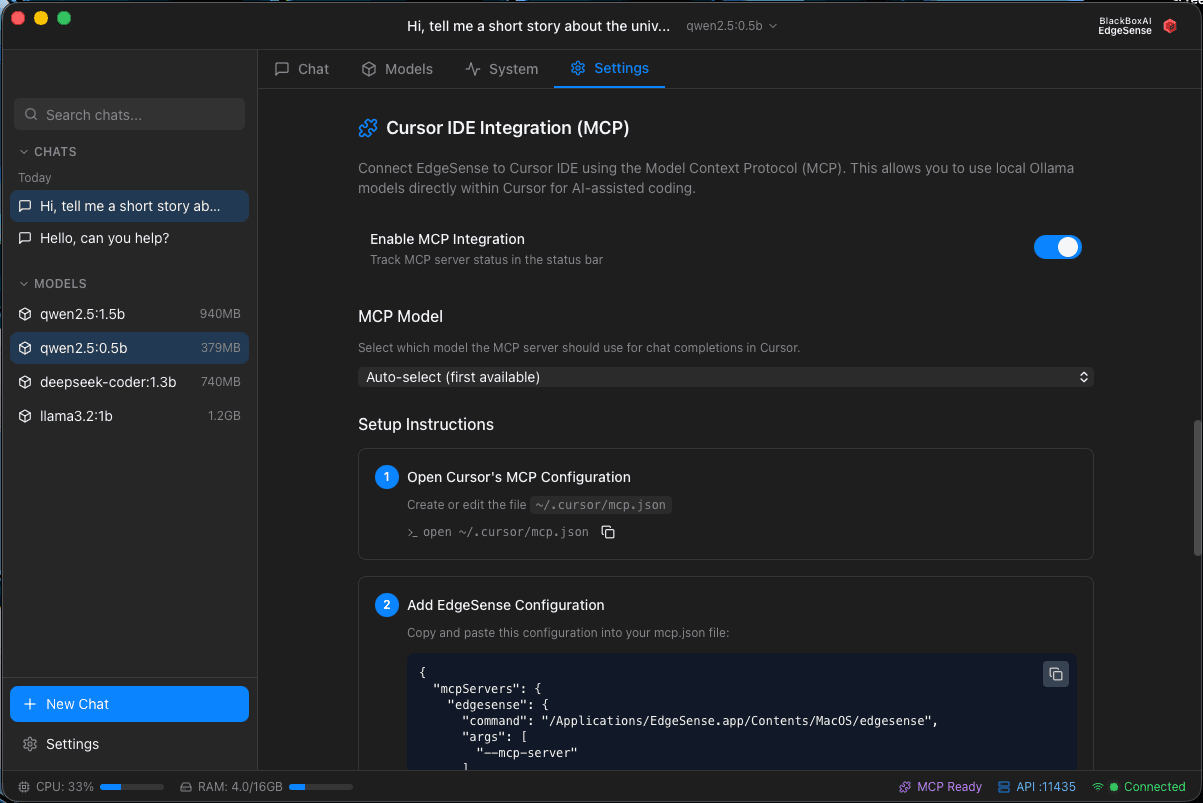
EdgeSense - MCP Server
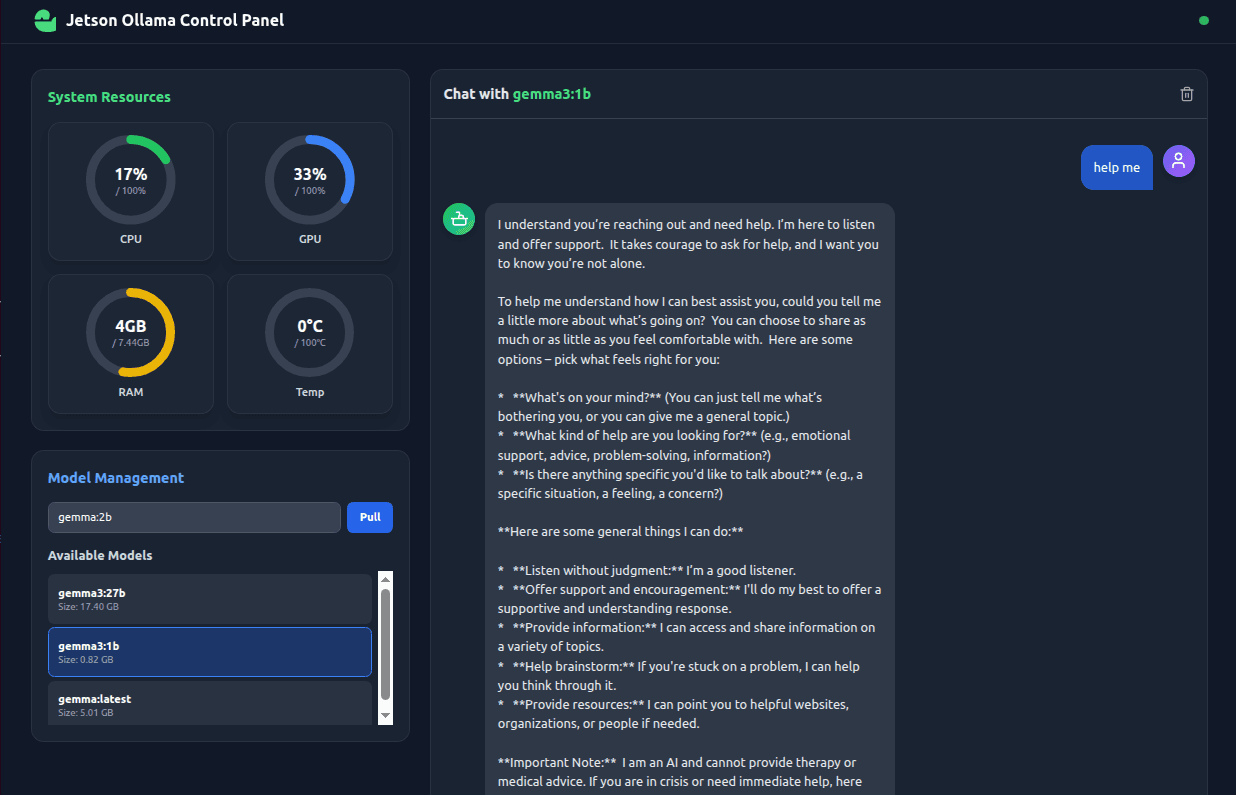
v0.2.0 Working Resourced and Selectable models
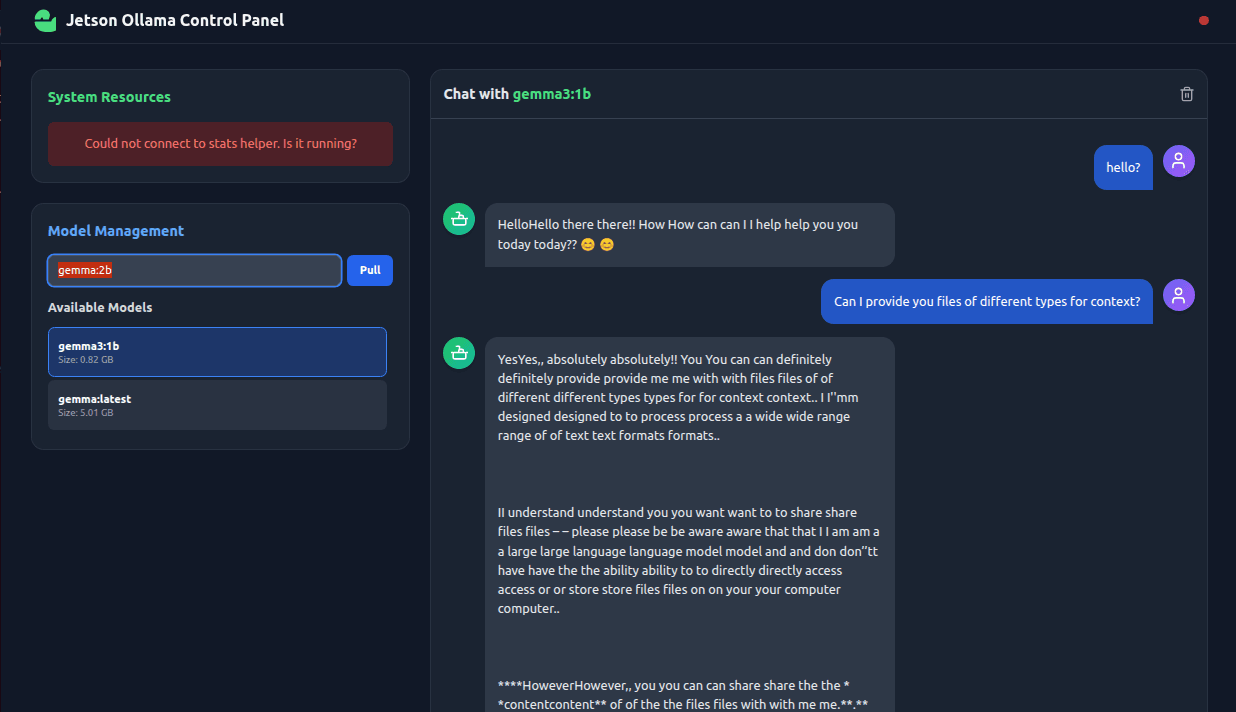
v0.1.0 Ollama front end with markdown rendering
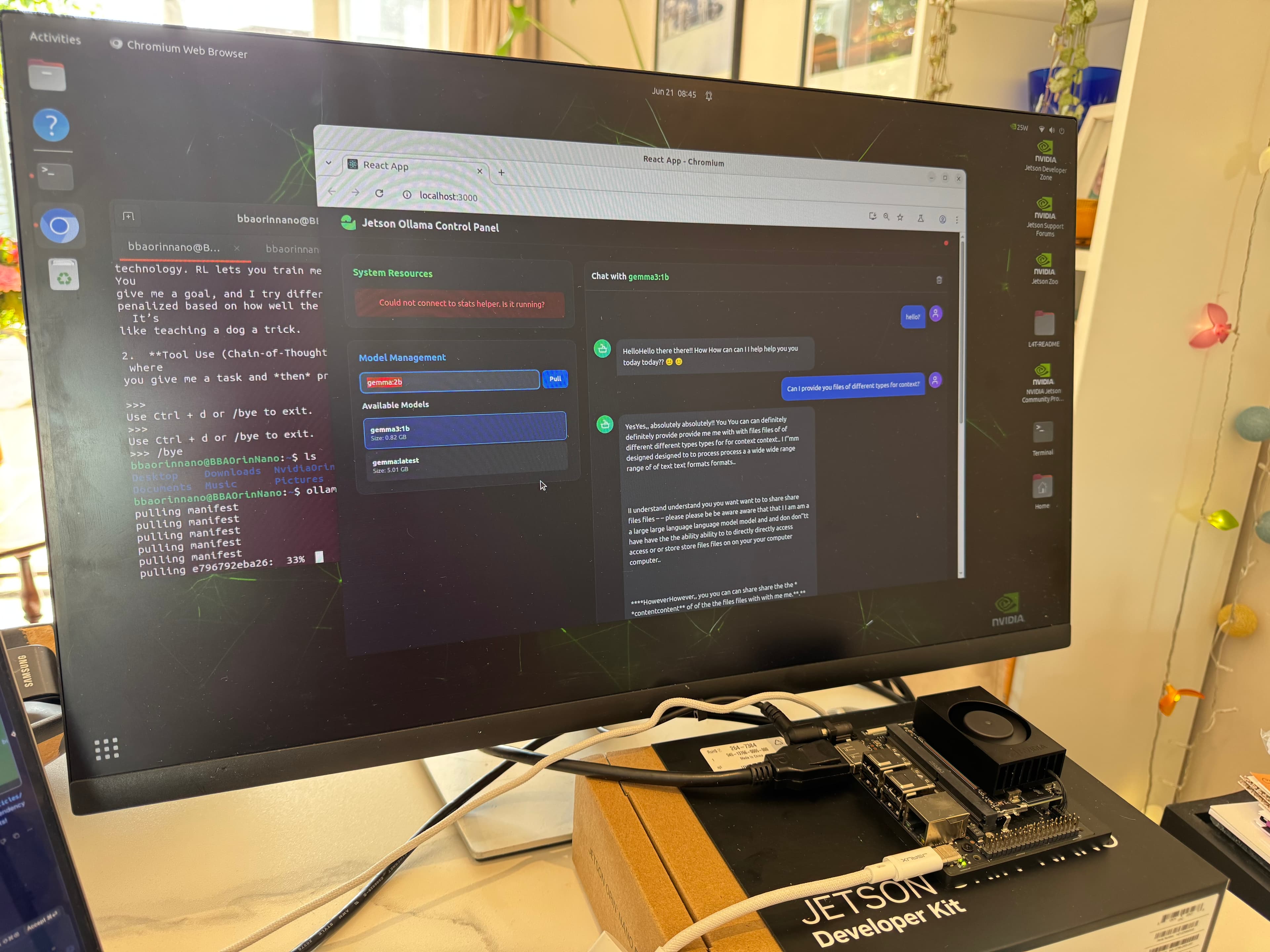
V0.1.0 Ollama front end working
TensorFlow and Ollama install complete

Nvidia Jetson Orin Nano
Loading updates...
Project Roadmap
Loading timeline...
Upcoming Features
As a user, I want to be able to view and follow detailed installation instructions for client software on Linux and Arduino devices because it will guide me through the necessary setup process. This will affect the EdgeSense Settings page and integrate installation guidance directly into the application. Additionally, I want to see the current host IP address displayed in the IoT Sensor Section because it will provide me with essential network information. These updates will ensure a seamless experience by offering clear, step-by-step instructions and accurate IP address information, enhancing my ability to successfully install and configure the software on my devices.Planned
Medium Priority
As a user, I want to be able to seamlessly connect and communicate with devices across different networks without relying on static IP addresses because an improved self-discovery feature will utilize API keys for device identification and communication. This will affect the backend system, specifically the `stats_server.py` for API key management, and the frontend, particularly the `frontend/src` for dynamic discovery and communication using API keys. Additionally, the configuration management scripts, such as `deploy_and_run.sh`, will be updated to support this new system.Planned
Medium Priority
As a user, I want to be able to navigate the settings page more efficiently by expanding or collapsing groups of related settings because it will organize numerous options into manageable subsections, improving the overall user experience. This change will affect the settings page, specifically the user interface where settings are displayed.Completed
Medium Priority
As a user, I want to be able to configure GPIO pins and device names through a client software configuration file because this will simplify the management of connected devices and allow for easy updates. Additionally, I want the ability to delete stored devices to maintain an organized and up-to-date system. This will affect the configuration management and device management modules, specifically impacting the configuration file found in the `NvidiaOrinNano/config/` directory and the device management UI in `DeviceConfig.js` within the `NvidiaOrinNano/frontend/src/` directory.Planned
Medium Priority
As a user, I want to be able to connect to and interact with online language models like Grok, OpenAI, Gemini, and Anthropic because this integration will allow me to leverage advanced AI capabilities directly from the application. This will affect the side panel and Models page by updating them to include dynamic listings of available online models. Additionally, I want a new section on the settings page to manage my API keys securely, ensuring easy and safe connectivity.Planned
Medium Priority
Known Issues
No known issues
Documents & Files
EdgeSense v0.1 MacOS Application
Install Document - ReadMe
Project Challenges
Challenge 1: Real-time System Monitoring
The first challenge was getting live CPU, GPU, and RAM data from the Jetson into the browser. The
Challenge 2: Managing Memory on a Constrained Device
The Jetson Orin Nano is powerful, but its 8 GB of RAM can be quickly consumed by larger language models. Early in testing, I found the system would become unresponsive or even freeze if I tried to load a model that was too large for the available memory.
Challenge 3: Smoothly Streaming Chat Responses
I wanted the chat to feel interactive, with the model's response appearing token by token, just like in popular applications. Ollama's API supports streaming, but handling this correctly on the frontend was tricky. Initial implementations resulted in garbled text or the entire response appearing at once.
The first challenge was getting live CPU, GPU, and RAM data from the Jetson into the browser. The
tegrastats utility provides this information, but it's a command-line tool.Challenge 2: Managing Memory on a Constrained Device
The Jetson Orin Nano is powerful, but its 8 GB of RAM can be quickly consumed by larger language models. Early in testing, I found the system would become unresponsive or even freeze if I tried to load a model that was too large for the available memory.
Challenge 3: Smoothly Streaming Chat Responses
I wanted the chat to feel interactive, with the model's response appearing token by token, just like in popular applications. Ollama's API supports streaming, but handling this correctly on the frontend was tricky. Initial implementations resulted in garbled text or the entire response appearing at once.
Project Solutions & Learnings
Learning: I learned that for security reasons, a browser cannot directly execute local commands. The solution was to create the Python Flask "stats helper" API. This reinforced the principle of using a simple, dedicated microservice to bridge gaps between different parts of a system.
Learning: I gained a much deeper understanding of how to work with streaming APIs in React. It required careful state management to append new chunks of data to the existing message and re-render the component efficiently, creating the smooth, "typing" effect I was aiming for.
Learning: Resource management is paramount on edge devices. This led to the implementation of the "RAM guard-rail" feature. Before allowing a user to chat, the frontend fetches the model's size from the Ollama API and checks it against the free system RAM reported by the stats helper. If there isn't enough memory (with a safety margin), the chat input is disabled. This simple check dramatically improved the stability and user experience of the application.
Learning: I gained a much deeper understanding of how to work with streaming APIs in React. It required careful state management to append new chunks of data to the existing message and re-render the component efficiently, creating the smooth, "typing" effect I was aiming for.
Learning: Resource management is paramount on edge devices. This led to the implementation of the "RAM guard-rail" feature. Before allowing a user to chat, the frontend fetches the model's size from the Ollama API and checks it against the free system RAM reported by the stats helper. If there isn't enough memory (with a safety margin), the chat input is disabled. This simple check dramatically improved the stability and user experience of the application.